6 Ways To Design The Ultimate Autism Training Experience Today
Creating an effective autism training program is crucial for fostering a supportive and inclusive environment. Here, we delve into six key strategies to design a training experience that empowers individuals to better understand and interact with those on the autism spectrum.
1. Understand the Autism Spectrum

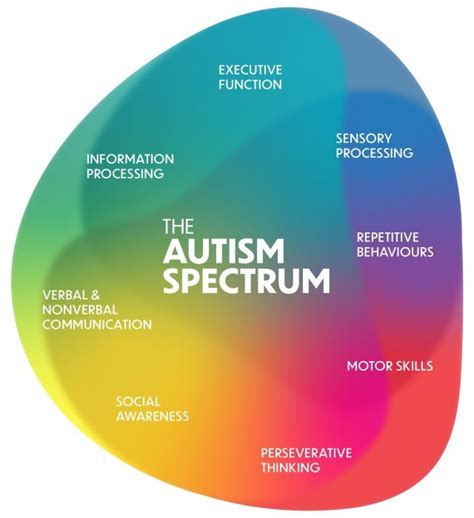
Autism, or Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that affects social communication, behavior, and sensory processing. It's important to emphasize that autism is a spectrum, meaning it presents differently in each individual. No two people with autism are exactly alike.
When designing your training, ensure that participants gain a comprehensive understanding of this spectrum. Highlight the diverse range of strengths, challenges, and unique traits associated with autism. By doing so, you promote an environment of acceptance and respect.
Key aspects to cover include:
- Social communication difficulties
- Restricted and repetitive behaviors
- Sensory processing differences
- The importance of early intervention
- Strategies for effective communication and support
2. Embrace Empathy and Understanding

Autism training should foster empathy and a deeper understanding of the daily experiences of individuals on the spectrum. Share personal stories and experiences to humanize the condition and encourage participants to see the world through a different lens.
Consider including:
- First-person accounts from individuals with autism
- Videos or documentaries showcasing the lives of people with autism
- Interactive activities that simulate sensory challenges
- Discussions on the impact of autism on families and caregivers
3. Focus on Practical Strategies

While understanding the theoretical aspects of autism is important, your training should also provide practical tools and strategies for effective interaction and support.
Cover topics such as:
- Communication techniques: visual supports, social stories, and alternative communication methods
- Behavior management: positive behavior support and understanding triggers
- Sensory processing: creating sensory-friendly environments and accommodating sensory needs
- Social skills development: teaching and facilitating social interactions
Provide participants with real-life scenarios and case studies to apply these strategies, ensuring they leave the training with a practical toolkit.
4. Emphasize the Importance of Individualization

One of the core principles of autism training should be the understanding that there is no one-size-fits-all approach. Each person with autism has unique needs and preferences.
Teach participants to:
- Observe and assess individual strengths and challenges
- Adapt their approach based on the person's needs
- Encourage self-advocacy and independence
By emphasizing individualization, you empower participants to create personalized support plans that truly make a difference.
5. Include Families and Caregivers

Autism training should extend beyond professionals and include families and caregivers. Their insights and experiences are invaluable.
Consider inviting:
- Parents or caregivers of individuals with autism to share their journeys
- Siblings or other family members to offer a different perspective
- Autism advocates or self-advocates to inspire and educate
Incorporating diverse voices ensures a well-rounded training experience.
6. Promote Ongoing Learning and Support
Autism training shouldn't be a one-time event. Encourage participants to continue their learning journey and provide resources for further exploration.
Offer suggestions such as:
- Books, blogs, and websites dedicated to autism
- Online courses or webinars for continued education
- Local support groups or autism-focused events
- Opportunities for mentorship or further training
By fostering a culture of ongoing learning, you create a community of knowledgeable and compassionate individuals.
Conclusion

Designing an effective autism training experience is a powerful step towards creating a more inclusive and understanding society. By following these six strategies, you can empower individuals to make a positive impact in the lives of those on the autism spectrum. Remember, it's not just about awareness; it's about action and creating meaningful change.
How can I ensure my training is accessible to all participants?

+
Consider providing training materials in various formats, such as written guides, videos, and audio recordings. Ensure that your training environment is inclusive and offers accommodations for participants with different needs. This may include providing quiet spaces, offering sensory-friendly options, and having trained staff available for support.
What are some common misconceptions about autism that I should address in my training?

+
Common misconceptions include the belief that all individuals with autism are non-verbal, lack empathy, or are intellectually disabled. It’s important to address these stereotypes and emphasize the diversity of the autism spectrum. Highlight the strengths and talents of individuals with autism, and provide examples of successful individuals who have autism.
How can I make my training interactive and engaging?

+
Incorporate a variety of activities and teaching methods to keep participants engaged. This can include group discussions, role-playing scenarios, hands-on activities, and interactive presentations. Break down complex concepts into simpler, more digestible chunks, and encourage participants to share their own experiences and ask questions.
What resources can I recommend to participants for further learning?

+
Recommend reputable websites, books, and organizations dedicated to autism awareness and support. Some examples include the Autism Society, Autism Speaks, and the National Autistic Society. Provide a list of recommended reading materials and online resources, and consider creating a community forum or social media group for ongoing discussions and support.
How can I measure the success and impact of my autism training program?

+
Implement pre- and post-training assessments to measure knowledge and attitude shifts. Collect feedback from participants to understand their learning experience and identify areas for improvement. Follow up with participants after a period of time to assess the practical application of the training and its long-term impact. Regularly review and update your training program based on feedback and evolving best practices.