Budget Of England
The budget of England is a complex and multifaceted topic that plays a crucial role in shaping the country's economic landscape. It involves careful planning, strategic allocation of resources, and consideration of various factors to ensure the nation's financial stability and growth. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of England's budget, exploring its components, processes, and the impact it has on the lives of its citizens.
Understanding the Budget Process
The budget process in England is a well-defined and structured mechanism that involves multiple stages and stakeholders. It begins with the formulation of the budget, where the government assesses the country's economic situation, sets financial goals, and identifies priorities for spending and taxation.
Key Steps in Budget Formulation:

- Economic Forecasting: Experts analyze economic trends, growth rates, and potential risks to estimate revenue and assess the financial needs of the country.
- Priority Setting: The government identifies critical areas such as healthcare, education, infrastructure, and social welfare, allocating funds accordingly.
- Revenue Generation: This step involves determining tax policies, rates, and potential new sources of revenue to fund the budget.
- Spending Proposals: Departments and agencies submit spending proposals, detailing their financial requirements for the upcoming fiscal year.
The Role of the Chancellor of the Exchequer

The Chancellor of the Exchequer is a vital figure in England's budget process. They are responsible for presenting the budget to Parliament and making crucial decisions regarding taxation, spending, and economic policies.
Key Responsibilities of the Chancellor:

- Budget Speech: The Chancellor delivers an annual budget speech, outlining the government's financial plans and highlighting key initiatives.
- Economic Management: They oversee the country's economic performance, making adjustments to policies as needed to promote stability and growth.
- Fiscal Policy: The Chancellor plays a pivotal role in determining tax rates, incentives, and measures to stimulate economic activity.
Revenue Sources

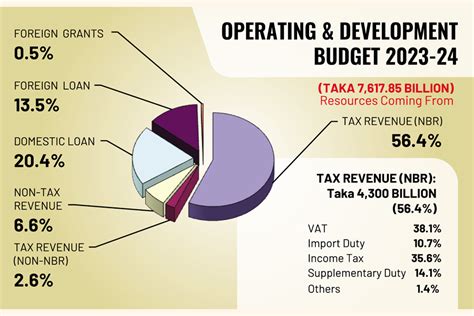
England's budget is primarily funded through a combination of taxes and other revenue streams. Understanding these sources is essential to grasp the financial landscape of the country.
Major Revenue Sources:

- Income Tax: This is a significant source of revenue, with rates varying based on income levels.
- Value Added Tax (VAT): VAT is applied to most goods and services, contributing a substantial portion to the budget.
- Corporate Taxes: Businesses operating in England pay corporate taxes, which are crucial for funding public services.
- Excise Duties: Taxes on specific goods like alcohol, tobacco, and fuel provide additional revenue.
- National Insurance Contributions: Employees and employers contribute to this fund, supporting social security and healthcare.
Spending Priorities

The allocation of funds in England's budget is a careful balancing act, ensuring that essential services are adequately funded while promoting economic growth and social welfare.
Key Spending Areas:

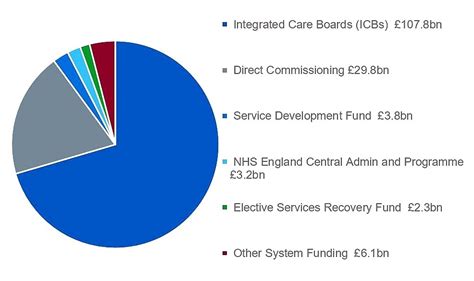
- Healthcare: The National Health Service (NHS) is a top priority, receiving substantial funding to provide universal healthcare to citizens.
- Education: Investing in education is vital for England's future, with funds allocated to schools, universities, and training programs.
- Social Welfare: Social security programs, pensions, and benefits for vulnerable individuals are crucial aspects of the budget.
- Infrastructure: Developing and maintaining infrastructure, including transportation, energy, and digital networks, is essential for economic growth.
- Defense and Security: Funding for defense forces and national security measures is a significant portion of the budget.
Budget Deficits and Surpluses

Budget deficits occur when government spending exceeds revenue, while surpluses arise when revenue exceeds spending. Managing these imbalances is a critical aspect of financial planning.
Strategies for Addressing Deficits:

- Spending Cuts: Reducing spending in certain areas to align with available revenue.
- Borrowing: The government may borrow money to cover deficits, which can be repaid over time.
- Tax Increases: Raising tax rates to generate more revenue and reduce the deficit.
Benefits of Budget Surpluses:
- Reduced national debt.
- Opportunities for tax cuts or increased spending on priority areas.
- Enhanced financial stability and creditworthiness.
Impact on Citizens
England's budget directly affects the lives of its citizens, influencing the availability and quality of public services, tax obligations, and economic opportunities.
Key Impacts on Citizens:

- Taxation: Citizens' tax contributions fund public services and infrastructure, impacting their disposable income.
- Public Services: The budget determines the level of funding for healthcare, education, and social welfare, affecting the accessibility and quality of these services.
- Economic Opportunities: Government spending on infrastructure and business incentives can create jobs and stimulate economic growth, benefiting citizens.
Budget Transparency and Accountability

Ensuring budget transparency and accountability is crucial to maintain public trust and effective governance.
Measures for Transparency and Accountability:

- Public Reports: The government publishes detailed budget reports, providing transparency on revenue, spending, and financial performance.
- Independent Audits: External audits ensure accurate financial reporting and identify potential areas of improvement.
- Parliamentary Scrutiny: Parliament plays a vital role in scrutinizing the budget, proposing amendments, and holding the government accountable.
Budget Challenges and Future Outlook
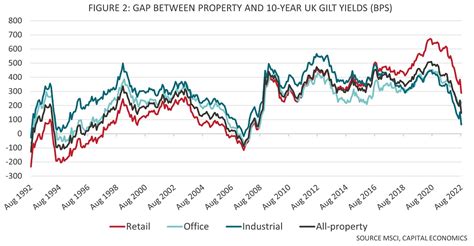
England's budget faces various challenges, including economic uncertainties, demographic shifts, and evolving social needs. Adapting to these challenges is essential for long-term financial stability.
Key Budget Challenges:
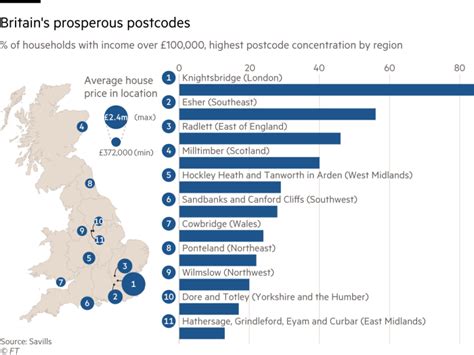
- Economic Uncertainty: Global economic fluctuations can impact England's revenue and spending plans.
- Demographic Changes: An aging population may strain social welfare and healthcare budgets.
- Technological Advancements: Investing in digital infrastructure and adapting to technological changes is crucial for future economic growth.
Conclusion

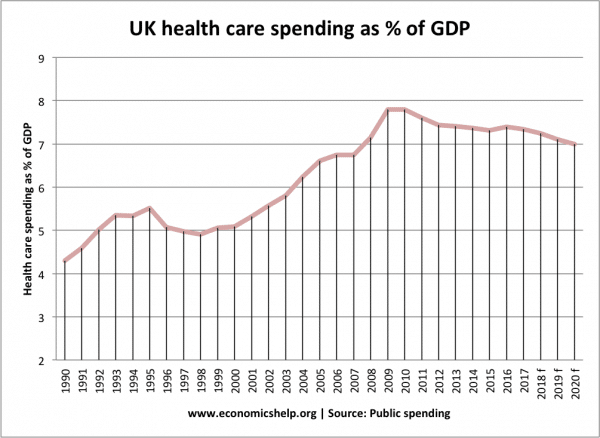
England's budget is a complex and dynamic entity, shaped by economic realities, social needs, and political decisions. It plays a pivotal role in the country's economic prosperity and the well-being of its citizens. By understanding the budget process, revenue sources, spending priorities, and the impact on individuals, we can appreciate the significance of responsible financial management in shaping a nation's future.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is the current budget deficit in England?

+
As of [Insert Year], the budget deficit in England stands at [Insert Amount]. This figure represents the gap between government spending and revenue.
How does the budget impact healthcare services in England?
+The budget plays a crucial role in funding the National Health Service (NHS). Adequate funding ensures the availability of essential healthcare services, including access to doctors, hospitals, and medications.
Are there any tax incentives for businesses in England’s budget?
+Yes, the budget often includes tax incentives and measures to encourage business growth and investment. These incentives can vary based on the government’s economic policies.
How does England’s budget compare to other countries in the EU?
+England’s budget is among the largest in the EU, reflecting its status as a major economic power. However, budget allocations and priorities can vary significantly between countries.
What measures are in place to ensure budget transparency in England?
+England has robust measures to ensure budget transparency, including public reports, independent audits, and parliamentary scrutiny. These mechanisms help maintain public trust and accountability.



