Dvla Reporting No Tax

Understanding the DVLA and Vehicle Taxation
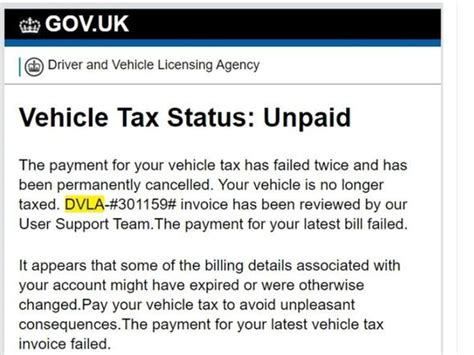
The DVLA, or the Driver and Vehicle Licensing Agency, is a government organization responsible for maintaining a database of all licensed drivers and registered vehicles in the United Kingdom. One of the key roles of the DVLA is to manage vehicle taxation, ensuring that vehicle owners pay the necessary taxes and fees associated with their vehicles. However, there are instances when vehicle owners may need to report issues related to vehicle tax, such as when the tax has expired or there is a discrepancy in the tax payment. This guide will walk you through the process of reporting no tax to the DVLA and provide insights into the steps you need to take.
Reporting No Tax: A Step-by-Step Guide

Step 1: Check Your Vehicle’s Tax Status
Before reporting no tax, it’s essential to verify the current tax status of your vehicle. You can easily check this online by visiting the DVLA’s vehicle tax check website. Simply enter your registration number, and the system will provide you with the following information:
- Whether your vehicle is currently taxed.
- The date of the last tax payment.
- The date the current tax period expires.
Note: It’s crucial to ensure that you have accurate and up-to-date information about your vehicle’s tax status before proceeding with any further steps.
Step 2: Identify the Reason for Reporting No Tax
There could be several reasons why you need to report no tax to the DVLA. Some common scenarios include:
- Expired Tax: If your vehicle’s tax has expired and you have not renewed it, you must report this to the DVLA to avoid penalties and ensure compliance.
- Incorrect Tax Payment: In some cases, there might be a discrepancy in the tax payment, such as an overpayment or an incorrect vehicle class being taxed. In such situations, reporting the issue to the DVLA is necessary to rectify the mistake.
- Change of Circumstances: If you have recently sold your vehicle, scrapped it, or made significant modifications that affect its tax status, you should report these changes to the DVLA to update their records.
Step 3: Gather Required Documentation
To report no tax to the DVLA, you will need to provide certain documents to support your claim. The specific documents required may vary depending on the reason for your report. Here are some common documents you might need:
- Vehicle Registration Document (V5C): This official document, also known as the logbook, contains important details about your vehicle, including its registration number, make, model, and previous owners.
- Proof of Identity: The DVLA may require you to provide proof of your identity, such as a valid driving license or passport.
- Proof of Address: You might need to submit a recent utility bill or bank statement as proof of your current address.
- Vehicle Ownership Documents: If you have recently purchased a vehicle or inherited it, you may need to provide relevant ownership documents.
- Supporting Evidence: Depending on the reason for your report, you might need additional evidence, such as receipts, correspondence, or photographs.
Note: Ensure that all documents are clear, legible, and up-to-date. It’s a good idea to make copies of your original documents to avoid any potential loss or damage during the reporting process.
Step 4: Contact the DVLA
Once you have gathered the necessary documentation, it’s time to contact the DVLA to report no tax. The DVLA offers various channels for communication, allowing you to choose the most convenient method:
- Online Reporting: The DVLA provides an online reporting system where you can submit your no-tax report. Visit their official website and follow the instructions to complete the online form. Ensure that you have all the required information and documents ready before starting the process.
- Telephone: If you prefer a more direct approach, you can call the DVLA’s customer service helpline. Their contact details can be found on their website. Be prepared to provide the relevant details and have your documents readily accessible during the call.
- Postal Reporting: In some cases, the DVLA may require you to send your report and supporting documents via post. Ensure that you use a secure and trackable delivery service to guarantee the safe arrival of your package.
Step 5: Follow Up and Resolution
After reporting no tax to the DVLA, it’s important to follow up on your case to ensure a timely resolution. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Processing Time: The DVLA aims to process no-tax reports as quickly as possible. However, the time taken for resolution may vary depending on the complexity of your case and the volume of reports they receive.
- Updates and Notifications: The DVLA will typically provide updates and notifications regarding the progress of your report. Keep an eye on your email or postal address for any correspondence from the DVLA.
- Further Action Required: In certain situations, the DVLA may request additional information or documentation from you. It’s crucial to respond promptly to their requests to avoid delays in resolving your case.
- Outcome and Next Steps: Once the DVLA has processed your report, they will inform you of the outcome. Depending on the reason for your report, they may provide instructions on how to rectify the issue, such as paying any outstanding tax or updating your vehicle’s details.
Common Issues and How to Resolve Them

Reporting no tax to the DVLA can sometimes lead to various issues and challenges. Here are some common problems you might encounter and guidance on how to resolve them:
- Expired Tax with No Reminder: If your vehicle’s tax has expired, and you did not receive a reminder notice from the DVLA, it’s essential to take immediate action. Contact the DVLA as soon as possible to report the expired tax and make the necessary arrangements to renew it.
- Overpayment of Tax: In some cases, you might have overpaid your vehicle tax due to a mistake or a change in circumstances. If this happens, report the overpayment to the DVLA, providing them with the relevant details and supporting evidence. They will guide you on the steps to reclaim the overpaid amount.
- Incorrect Vehicle Classification: If you believe that your vehicle has been incorrectly classified for tax purposes, resulting in an overpayment or underpayment, report this issue to the DVLA. Explain the reason for the incorrect classification and provide any necessary documentation to support your claim.
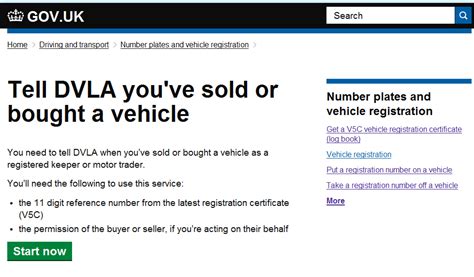
- Vehicle Sold or Scrapped: If you have sold your vehicle or had it scrapped, it’s crucial to inform the DVLA to avoid any further tax liabilities. Provide them with the details of the new owner (if sold) or the disposal method (if scrapped). This will ensure that your records are updated, and you are no longer responsible for the vehicle’s tax.
Additional Tips for a Smooth Reporting Process
To ensure a smooth and efficient reporting process, consider the following tips:
- Keep Your Documents Organized: Maintain a dedicated file or folder for all your vehicle-related documents, including registration, insurance, and tax-related papers. This will make it easier to access the necessary information and documents when reporting no tax.
- Set Reminders: Avoid forgetting important tax deadlines by setting reminders on your calendar or using reminder apps. This simple practice can help ensure that you renew your vehicle tax on time and avoid any potential penalties.
- Stay Informed: Keep yourself updated on any changes or updates to vehicle tax regulations. The DVLA’s website often provides valuable information and guidance on the latest tax-related matters. Staying informed can help you navigate the reporting process more effectively.
- Seek Professional Assistance: If you encounter complex issues or have difficulty understanding the reporting process, consider seeking assistance from a professional. Tax advisors or legal experts specializing in vehicle taxation can provide valuable guidance and support.
Conclusion

Reporting no tax to the DVLA is a crucial step in maintaining compliance with vehicle taxation regulations. By following the step-by-step guide outlined above, you can navigate the reporting process efficiently and ensure that your vehicle’s tax status is up-to-date. Remember to gather the required documentation, contact the DVLA through their preferred channels, and stay proactive in following up on your report. With proper attention and timely action, you can resolve any tax-related issues and continue driving with peace of mind.
FAQ

How often do I need to renew my vehicle tax?

+
The frequency of vehicle tax renewal depends on the tax class and the method of payment chosen. Typically, vehicle tax is renewed annually, but you can also opt for shorter periods, such as six months. It’s essential to renew your tax before the current period expires to avoid penalties.
What happens if I drive without valid vehicle tax?

+
Driving without valid vehicle tax is illegal and can result in penalties. If caught by the authorities, you may face a fine, and your vehicle could be clamped or even impounded. It’s crucial to ensure that your vehicle tax is up-to-date to avoid these consequences.
Can I report no tax online if I don’t have internet access?
+
Yes, you can still report no tax to the DVLA even if you don’t have internet access. The DVLA provides alternative methods, such as telephone reporting or postal reporting. Simply contact their customer service helpline or send your report and supporting documents via post.
How long does it take for the DVLA to process a no-tax report?

+
The processing time for a no-tax report can vary depending on the complexity of your case and the volume of reports received by the DVLA. While they aim to process reports as quickly as possible, it’s advisable to allow sufficient time for the resolution, especially if further investigation is required.
Can I reclaim overpaid vehicle tax?

+
Yes, if you have overpaid your vehicle tax, you can reclaim the excess amount. Contact the DVLA and provide them with the necessary details and supporting evidence. They will guide you through the reimbursement process, which may involve completing specific forms and providing additional documentation.