Esol Level 2: The Ultimate Guide To Mastering English Grammar

An Introduction to English Grammar

English grammar can be a complex and sometimes daunting topic, especially for those learning English as a second language. However, with the right approach and resources, mastering English grammar is within your reach. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the key concepts and rules of English grammar, providing you with the tools and knowledge to improve your language skills and communicate effectively. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to enhance your existing knowledge, this ultimate guide will take you through the essential grammar topics at Esol Level 2.
Parts of Speech: The Building Blocks of Grammar

To understand English grammar, it’s crucial to grasp the concept of parts of speech. These are the different word categories that make up sentences and determine their structure. Here’s an overview of the main parts of speech:
Nouns

Nouns are words that refer to people, places, things, or ideas. They are the foundation of sentences and can be used as subjects, objects, or complements. There are two main types of nouns:
- Common Nouns: These refer to general things or concepts, such as “book,” “city,” or “happiness.”
- Proper Nouns: Proper nouns are specific names of people, places, or things, like “John,” “Paris,” or “Amazon.” Proper nouns are usually capitalized.
Verbs

Verbs are action words that describe what a subject is doing or experiencing. They indicate actions, states of being, or occurrences. Verbs are essential for expressing thoughts and actions in sentences. Some examples of verbs include “run,” “think,” “be,” and “feel.”
Adjectives

Adjectives modify nouns or pronouns by providing additional information about their qualities, quantity, or state. They describe or give more details about the noun they are associated with. For instance, “beautiful,” “old,” and “happy” are adjectives.
Adverbs

Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, providing information about manner, time, place, degree, or frequency. They answer questions like “how,” “when,” “where,” or “to what extent.” Adverbs often end with the suffix “-ly,” such as “quickly,” “happily,” or “soon.”
Pronouns

Pronouns are words used in place of nouns to avoid repetition. They refer to specific people, places, or things already mentioned or implied. Common pronouns include “I,” “you,” “he,” “she,” “it,” “they,” and “them.”
Prepositions

Prepositions are words that show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and another word in a sentence. They indicate location, direction, time, or possession. Examples of prepositions include “in,” “on,” “at,” “by,” and “with.”
Conjunctions

Conjunctions are joining words that connect words, phrases, or clauses. They can be coordinating conjunctions (e.g., “and,” “but,” “or”) or subordinating conjunctions (e.g., “because,” “although,” “while”). Conjunctions help create complex sentences and express relationships between ideas.
Interjections

Interjections are words or phrases used to express strong feelings or emotions. They are often exclamatory and can stand alone or be part of a sentence. Examples of interjections include “Wow!” “Ouch!” and “Hey!”
Sentence Structure: Building Blocks of Communication

Understanding sentence structure is vital for constructing meaningful and grammatically correct sentences. Here’s a breakdown of the different types of sentences:
Simple Sentences
A simple sentence consists of a single independent clause, containing a subject and a verb. It expresses a complete thought and can stand alone. For example: “The cat chased the mouse.”
Compound Sentences

Compound sentences combine two or more independent clauses using coordinating conjunctions. Each clause can stand alone as a simple sentence. Compound sentences are joined by words like “and,” “but,” “or,” “yet,” “for,” and “so.” For instance: “The sun shone brightly, and the birds sang merrily.”
Complex Sentences
Complex sentences consist of one independent clause and one or more dependent clauses. Dependent clauses cannot stand alone and are often introduced by subordinating conjunctions. For example: “Although it was raining, we decided to go for a walk.”
Compound-Complex Sentences
Compound-complex sentences combine elements of compound and complex sentences. They have multiple independent clauses and at least one dependent clause. For instance: “The cat chased the mouse, but it escaped, so the cat had to find another way to catch it.”
Verb Tenses: Mastering Time and Action

Verb tenses are crucial for indicating the time and duration of actions or states. Here’s an overview of the main verb tenses:
Present Tense
The present tense describes actions or states that are happening now or that are generally true. It can also be used for future actions when no specific time is mentioned. Examples include: “I live in a beautiful city” and “We are going to the park tomorrow.”
Past Tense
The past tense is used to describe actions or states that have already happened. It indicates that the action or state is completed in the past. For instance: “I lived in a small town” and “They played football yesterday.”
Future Tense
The future tense refers to actions or states that will happen at a later time. It can be formed using will/shall or be going to. Examples include: “I will finish my homework soon” and “She is going to travel next month.”
Perfect Tenses
Perfect tenses describe actions that are complete or perfect in relation to a specific time. There are three perfect tenses: present perfect, past perfect, and future perfect. They are formed using the verb “have” and the past participle of the main verb. Examples include: “I have finished my homework” (present perfect) and “They had already left by the time we arrived” (past perfect).
Progressive Tenses
Progressive tenses indicate ongoing or continuous actions. They are formed using the verb “be” (am, is, are, was, were) and the present participle of the main verb (ending in “-ing”). Examples include: “I am studying for my exam” (present progressive) and “They were running towards the finish line” (past progressive).
Agreement and Consistency: Ensuring Cohesion
Agreement and consistency are essential principles in English grammar to ensure that sentences are grammatically correct and coherent. Here’s a closer look at these concepts:
Subject-Verb Agreement
Subject-verb agreement ensures that the subject and verb in a sentence agree in number and person. In simple terms, a singular subject requires a singular verb, and a plural subject requires a plural verb. For example: “The boy plays football” (singular subject and verb) and “The boys play football” (plural subject and verb).
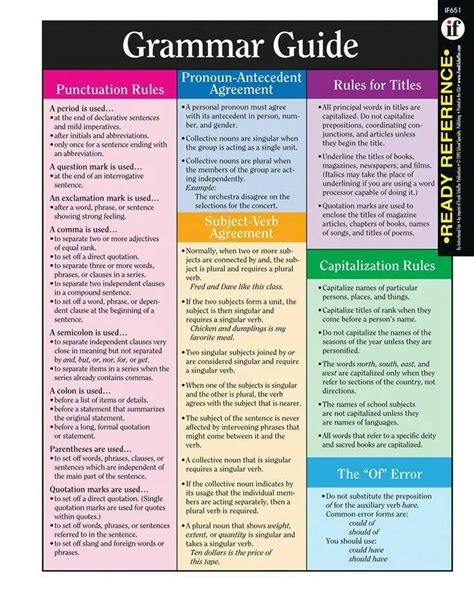
Pronoun-Antecedent Agreement
Pronoun-antecedent agreement ensures that pronouns and their antecedents (the nouns they refer to) agree in number, person, and gender. For instance: “Each student must bring their own supplies” (incorrect, should be “his or her own supplies” to agree with the singular antecedent “student”).
Consistency in Tense and Voice
Consistency in tense and voice is crucial for maintaining clarity and coherence in writing. It’s important to use the same tense throughout a sentence or paragraph unless there is a specific reason to change tenses. Similarly, maintaining consistency in voice (active or passive) helps create a smooth flow in your writing.
Punctuation: Adding Clarity and Emphasis

Punctuation marks are essential for adding clarity, structure, and emphasis to your writing. Here are some common punctuation marks and their uses:
- Period (Full Stop): Used to indicate the end of a declarative sentence or to create an abbreviation.
- Comma: Used to separate items in a list, introduce a clause, or provide a pause in a sentence.
- Question Mark: Indicates a direct question.
- Exclamation Mark: Expresses strong emotion, surprise, or emphasis.
- Apostrophe: Used for contractions, possessives, and plurals of lowercase letters.
- Quotation Marks: Enclose direct speech or quotations.
- Colon: Introduces a list, explanation, or quotation.
- Semicolon: Connects two independent clauses or separates items in a complex list.
Common Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them

While English grammar can be complex, there are some common mistakes that many people make. Being aware of these mistakes can help you improve your grammar skills:
- Subject-Verb Disagreement: Ensure that the subject and verb agree in number and person.
- Misuse of Pronouns: Be careful with pronoun-antecedent agreement and choose the correct pronoun to match the antecedent.
- Run-on Sentences: Avoid combining multiple independent clauses without proper punctuation or conjunctions.
- Fragmented Sentences: Ensure that each sentence expresses a complete thought and has a subject and verb.
- Confusing Verb Tenses: Pay attention to verb tenses and maintain consistency throughout your writing.
- Incorrect Punctuation: Learn the proper use of punctuation marks to enhance the clarity and readability of your writing.
Enhancing Your Grammar Skills: Tips and Resources

Improving your grammar skills is an ongoing process, and there are various resources and strategies you can use:
- Practice: Regularly practice writing and speaking in English. The more you use the language, the better your grammar will become.
- Read: Reading a variety of texts, such as books, newspapers, and online articles, can expose you to correct grammar usage and improve your understanding.
- Use Grammar Checkers: Grammar checkers, like Grammarly or ProWritingAid, can help identify and correct grammar mistakes in your writing.
- Online Grammar Courses: Enroll in online grammar courses or tutorials to learn specific grammar topics in a structured manner.
- Join Language Communities: Engage with language learning communities or forums where you can discuss grammar-related questions and seek feedback.
- Grammar Workbooks: Workbooks specifically designed for grammar practice can provide targeted exercises to improve your skills.
Conclusion

Mastering English grammar is a rewarding journey that enhances your communication skills and allows you to express yourself effectively. By understanding the parts of speech, sentence structure, verb tenses, and other grammar concepts, you can construct well-formed sentences and convey your ideas clearly. Remember to practice regularly, seek feedback, and utilize the resources available to you. With dedication and a strong foundation in grammar, you’ll be able to navigate the complexities of the English language with confidence.
FAQ

What are the most common parts of speech in English grammar?
+The most common parts of speech in English grammar are nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
How can I improve my verb tense accuracy in writing?
+To improve verb tense accuracy, practice writing in different tenses and pay attention to the context and time frames of your sentences. Regularly review verb conjugation rules and use resources like grammar books or online guides to reinforce your understanding.
What are some common mistakes to avoid in English grammar?
+Common grammar mistakes include subject-verb disagreement, pronoun-antecedent mismatch, run-on sentences, fragmented sentences, and inconsistent verb tenses. Being aware of these mistakes and practicing proper grammar usage can help you avoid them.
Are there any online resources for learning English grammar?
+Yes, there are numerous online resources available for learning English grammar. Websites like Grammarly, Khan Academy, and BBC Learning English offer interactive lessons, quizzes, and exercises to improve your grammar skills. Additionally, YouTube has many grammar tutorial videos.
How can I improve my sentence structure and complexity?
+To improve sentence structure and complexity, focus on varying sentence lengths and types. Practice writing compound and complex sentences, and experiment with different sentence patterns. Reading extensively and analyzing the sentence structure of well-written texts can also enhance your skills.