Planning Permission For Extension

When you're considering extending your home, one of the first steps is to ensure you have the necessary planning permission. This process can seem daunting, but with the right information and preparation, it can be a smooth and successful journey. In this blog post, we'll guide you through the process of obtaining planning permission for your extension, covering everything from understanding the regulations to submitting your application.
Understanding the Planning System

The planning system is in place to regulate the development and use of land and buildings, ensuring that any changes made to the environment are in the best interest of the community and the local area. It's important to familiarize yourself with the planning system and its purpose before starting your extension project.
Permitted Development Rights

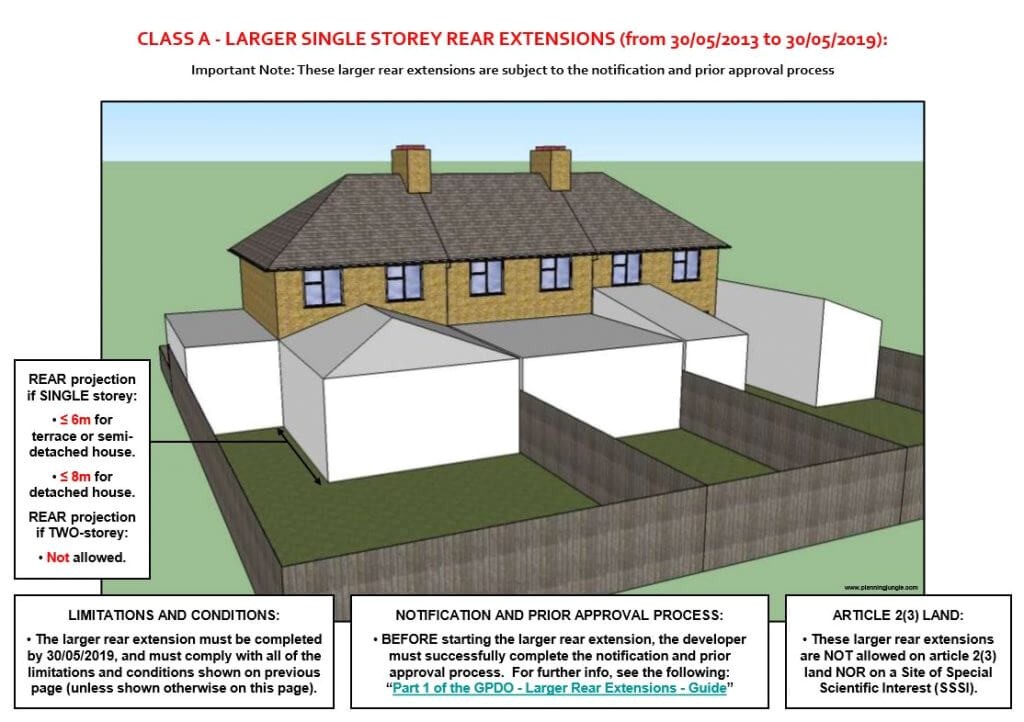
Before diving into the planning permission process, it's worth checking if your proposed extension falls under permitted development rights. These rights allow certain types of development to take place without the need for a full planning application. However, there are limits and conditions to these rights, so it's crucial to understand the specific regulations for your area.
Some common permitted development rights for house extensions include:
- Single-story rear extensions up to a certain size.
- Roof extensions and loft conversions.
- Garage conversions.
Check the government's planning portal for detailed information on permitted development rights and the specific regulations for your country.
Planning Constraints
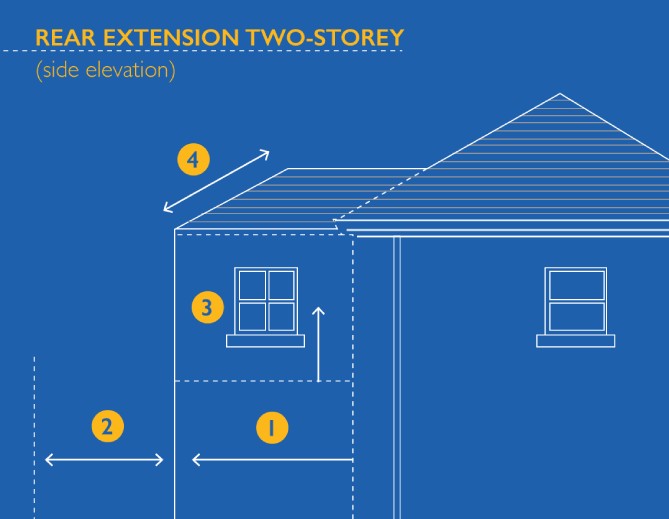
It's essential to be aware of any planning constraints that may affect your property. These constraints could include:
- Conservation Areas: Areas designated to protect the special architectural or historic interest of a place. Extensions in these areas may have stricter requirements.
- Listed Buildings: Properties that are of special architectural or historic interest and are protected by law. Any alterations to listed buildings require listed building consent.
- Tree Preservation Orders (TPOs): Orders made to protect specific trees or groups of trees. If your extension work involves removing or pruning trees, you may need to seek permission.
Check with your local planning authority or local council to determine if your property is subject to any planning constraints.
Assessing Your Property and Preparing a Plan

Before submitting a planning application, it's crucial to assess your property and prepare a detailed plan for your extension. This plan will form the basis of your application and will help you understand the feasibility of your project.
Site Survey

Conduct a comprehensive site survey to gather information about your property and its surroundings. This survey should include:
- Measuring the dimensions of your existing property and the proposed extension.
- Identifying any existing structures, such as outbuildings or boundary walls.
- Noting the proximity of your property to neighboring buildings and any potential issues with access or privacy.
- Assessing the condition of the ground and any potential drainage or foundation issues.
Designing Your Extension
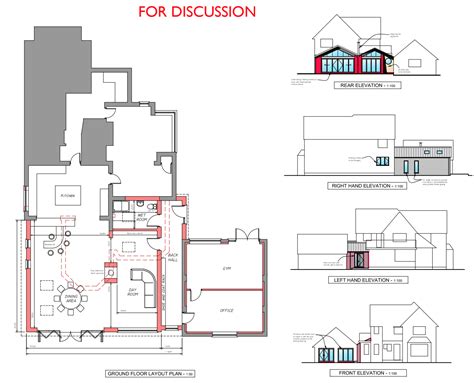
Work with an architect or designer to create a detailed plan for your extension. This plan should include:
- Floor plans, including the layout of the new space and any proposed alterations to the existing property.
- Elevations, showing the external appearance of the extension from different angles.
- Section drawings, which provide a cross-sectional view of the building, helping to illustrate the internal structure and any changes to the roof.
Your architect or designer should also be able to advise you on any specific requirements or considerations for your extension, such as:
- Window and door placement.
- Roof design and materials.
- Any necessary structural alterations.
Preparing Your Planning Application

Once you have a detailed plan for your extension, it's time to prepare your planning application. This application will be submitted to your local planning authority, who will assess it against the relevant planning policies and guidelines.
Application Forms and Fees

You can find the necessary application forms and guidance on the Planning Portal or your local council's website. Make sure to complete the forms accurately and provide all the required information, including:
- A description of the proposed development.
- The address and location of the property.
- The name and contact details of the applicant.
- Any supporting documents, such as site plans, design drawings, and planning statements.
There is usually a fee associated with submitting a planning application, which varies depending on the size and nature of the development. Check with your local planning authority for the correct fee.
Supporting Documentation

In addition to the application form, you'll need to provide a range of supporting documentation to strengthen your case. This may include:
- Site Plans: Detailed drawings showing the location of the proposed extension in relation to the existing property and its surroundings.
- Design and Access Statement: A document explaining how your proposed development meets the relevant planning policies and guidelines. It should also address any potential impacts on the local area and how these have been considered in the design.
- Neighbor Consultation: Evidence that you have consulted with your neighbors about the proposed extension. This could be in the form of letters or a summary of responses received.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: If your extension is likely to have a significant environmental impact, you may need to submit an assessment outlining the potential effects and any measures you plan to take to mitigate them.
Submitting Your Application
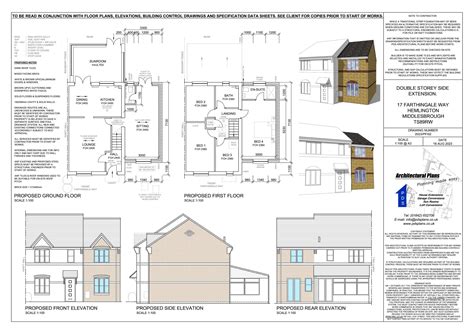
Once you have gathered all the necessary documentation, it's time to submit your planning application. You can do this online through the Planning Portal or by delivering the physical application to your local planning authority.
Make sure to keep a copy of your application for your records and consider informing your neighbors about the submission to avoid any potential delays or objections.
The Planning Decision

After submitting your application, the planning authority will assess it against the relevant planning policies and guidelines. This process can take several weeks or even months, depending on the complexity of your proposal and the workload of the planning department.
During this time, the planning authority may request additional information or clarification on certain aspects of your application. It's important to respond promptly to these requests to keep the process moving forward.
Planning Decision Outcomes

There are several possible outcomes for your planning application:
- Approval: Your application is approved as submitted, and you can proceed with your extension project.
- Approval with Conditions: Your application is approved, but certain conditions must be met before you can start construction. These conditions could include design changes, environmental measures, or other specific requirements.
- Deferred Decision: The planning authority may need more time to consider your application or await further information. In this case, they will notify you of the deferral and provide an updated decision date.
- Refusal: Your application is refused, and you will receive a written decision outlining the reasons for the refusal. You have the right to appeal this decision, but it's advisable to seek professional advice before doing so.
Appealing a Refusal
If your planning application is refused, you have the right to appeal the decision. The process for appealing varies depending on your location, but it typically involves submitting additional information and arguments to support your case.
It's strongly recommended to seek professional advice from a planning consultant or solicitor who specializes in planning appeals. They can guide you through the process and increase your chances of a successful appeal.
Working with a Planning Consultant

Hiring a planning consultant can be beneficial, especially if your extension project is complex or if you anticipate potential planning issues. A consultant can provide expert advice and guidance throughout the planning process, helping you navigate the regulations and increase your chances of a successful application.
Planning consultants can assist with:
- Interpreting planning policies and guidelines.
- Preparing a strong planning application.
- Negotiating with the planning authority.
- Representing your interests during the appeal process.
Conclusion

Obtaining planning permission for your extension can be a complex process, but with careful preparation and a thorough understanding of the regulations, you can increase your chances of a successful outcome. Remember to check your permitted development rights, assess your property, prepare a detailed plan, and submit a comprehensive planning application. Working with professionals, such as architects, designers, and planning consultants, can also greatly improve your chances of getting the go-ahead for your extension project.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is the difference between planning permission and building regulations approval?
+
Planning permission is required to ensure that your proposed development complies with local planning policies and guidelines. Building regulations approval, on the other hand, is necessary to ensure that your extension meets the necessary structural and safety standards.
How long does the planning permission process typically take?

+
The planning permission process can vary in duration depending on the complexity of your proposal and the workload of the planning department. It can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months.
Can I start building my extension before receiving planning permission?

+
No, it is illegal to start construction without obtaining the necessary planning permission. Doing so could result in enforcement action and the requirement to demolish any unauthorized works.
Are there any exceptions to the planning permission requirements for house extensions?
+Yes, certain types of house extensions may fall under permitted development rights, which allow for certain developments without the need for a full planning application. However, there are limits and conditions to these rights, so it’s important to check the specific regulations for your area.
What happens if my planning application is refused?
+If your planning application is refused, you have the right to appeal the decision. It’s recommended to seek professional advice from a planning consultant or solicitor who can guide you through the appeal process.