Ultimate Guide: 5Step Parking Design

Creating an Efficient and Organized Parking Space

Designing an effective parking layout is crucial for any commercial or residential property. A well-planned parking area not only enhances the aesthetics of the space but also ensures a smooth flow of traffic and maximizes the available space. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the five essential steps to create an efficient parking design.
Step 1: Assess the Site and User Requirements

Before you begin designing your parking layout, it is essential to evaluate the site and understand the specific needs of the users. This step will help you create a parking space that is functional, safe, and convenient.
Site Assessment

Topography: Consider the natural features of the land, such as slopes, trees, and water bodies. These elements can influence the layout and accessibility of your parking area.
Soil Conditions: Understand the soil type and its bearing capacity. This information is crucial for determining the type of pavement and the depth of foundation required.
Climate: Take into account the local climate, including the average temperature, rainfall, and snow accumulation. This will help you choose the appropriate pavement materials and drainage systems.
Existing Infrastructure: Evaluate any existing buildings, roads, or utilities on the site. You need to ensure that your parking design integrates seamlessly with the existing infrastructure.
User Requirements

Vehicle Types: Identify the types of vehicles that will be using the parking space. This includes cars, motorcycles, bicycles, and potentially larger vehicles like trucks or buses.
Parking Demand: Estimate the number of parking spaces required based on the expected number of users. Consider peak hours and special events that may require additional parking capacity.
Accessibility: Ensure that your design accommodates the needs of all users, including those with disabilities. Provide designated accessible parking spaces and ensure clear pathways for easy navigation.
Traffic Flow: Analyze the flow of traffic within the parking area. Design entry and exit points that minimize congestion and allow for smooth movement of vehicles.
Step 2: Determine the Parking Layout

Once you have a clear understanding of the site and user requirements, it’s time to start planning the layout of your parking space. This step involves deciding on the arrangement of parking stalls, aisles, and access points.
Parking Stall Layout
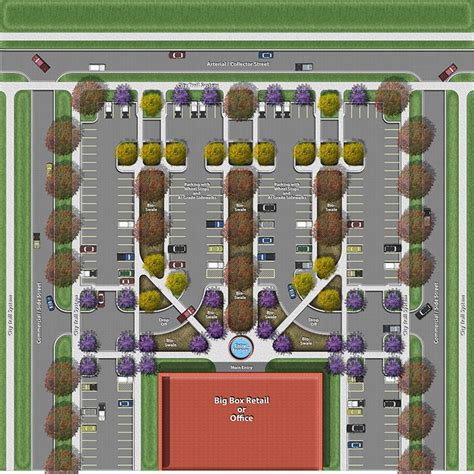
Stall Size: Determine the standard size of parking stalls based on the vehicle types and local regulations. Consider providing larger stalls for SUVs or trucks if necessary.
Stall Arrangement: Decide on the arrangement of parking stalls. Common arrangements include angle parking, perpendicular parking, and parallel parking.
Accessible Stalls: Allocate a sufficient number of accessible parking stalls based on local regulations and the expected demand. Ensure these stalls are properly marked and located close to building entrances.
Aisles and Access Points

Aisle Width: Determine the appropriate width for aisles based on the expected vehicle size and traffic flow. Wider aisles allow for better maneuverability and emergency access.
Access Points: Plan the entry and exit points for the parking area. Ensure these points are clearly marked and provide adequate visibility for drivers. Consider implementing one-way traffic flow to prevent congestion.
Step 3: Select the Pavement Type

The choice of pavement material is crucial for the durability and aesthetics of your parking area. Different pavement types have varying levels of strength, permeability, and maintenance requirements.
Asphalt Pavement

Advantages: Asphalt is a popular choice due to its cost-effectiveness, ease of installation, and ability to provide a smooth surface. It is also flexible and can accommodate temperature changes.
Considerations: Regular maintenance is required to prevent cracks and potholes. Asphalt may not be suitable for areas with heavy traffic or heavy loads, as it can deform over time.
Concrete Pavement

Advantages: Concrete offers excellent durability and can withstand heavy traffic and loads. It is also low-maintenance and has a longer lifespan compared to asphalt.
Considerations: Concrete is more expensive to install and requires specialized equipment. It is less flexible than asphalt and may require jointing to accommodate temperature changes.
Pervious Pavement

Advantages: Pervious pavement is an environmentally friendly option as it allows rainwater to infiltrate the ground, reducing runoff and improving water quality.
Considerations: Pervious pavement requires a well-designed sub-base and proper maintenance to prevent clogging. It may not be suitable for areas with high traffic volumes or heavy loads.
Step 4: Implement Drainage Systems

Effective drainage is essential to prevent water accumulation and potential flooding in your parking area. A well-designed drainage system will ensure the longevity of your pavement and improve the safety of users.
Surface Drainage
Grading: Ensure the parking area is properly graded to direct water towards drainage channels or catch basins.
Catch Basins: Install catch basins at low points to collect and channel water away from the parking area.
Drainage Channels: Use drainage channels or swales to convey water to catch basins or other drainage structures.
Subsurface Drainage

Subbase Preparation: Prepare a well-compacted subbase layer to facilitate water drainage and prevent soil erosion.
Perforated Pipes: Install perforated pipes or drainage tiles within the subbase to collect and convey water away from the pavement.
Geotextile Fabric: Consider using geotextile fabric to separate the subbase from the pavement, preventing fines from clogging the drainage system.
Step 5: Add Safety and Wayfinding Features

A well-designed parking area should prioritize the safety and convenience of users. Implement safety features and wayfinding elements to enhance the user experience and prevent accidents.
Safety Features

Lighting: Ensure adequate lighting throughout the parking area, especially in darker areas or during evening hours.
Security Cameras: Install security cameras to monitor the parking area and deter potential criminal activity.
Emergency Exits: Clearly mark emergency exits and provide easy access to them. Ensure these exits are well-lit and free from obstruction.
Speed Bumps: Consider installing speed bumps or other traffic-calming measures to slow down vehicles and prevent accidents.
Wayfinding Elements
Signage: Provide clear and visible signage to guide users to their parking spots, building entrances, and other important locations.
Aisle Markings: Use painted lines or markers to clearly define aisles and parking stalls.
Color Coding: Implement a color-coding system to help users identify different parking areas or reserved spaces.
Guideposts: Install guideposts or bollards to delineate pedestrian pathways and prevent vehicles from encroaching on them.
Conclusion

Designing an efficient parking layout requires careful consideration of various factors, including site conditions, user requirements, pavement selection, drainage systems, and safety features. By following these five steps, you can create a well-organized and functional parking space that meets the needs of users and enhances the overall experience.
What are the key factors to consider when designing a parking layout for a residential complex?
+
When designing a parking layout for a residential complex, consider factors such as the number of residents, their parking habits, and the available space. Ensure a balance between resident parking and visitor parking, and provide clear signage to guide users to their designated areas.
How can I ensure effective drainage in my parking area during heavy rainfall?
+
To ensure effective drainage during heavy rainfall, implement a combination of surface and subsurface drainage systems. Proper grading, catch basins, and perforated pipes will help convey water away from the parking area, preventing flooding and water accumulation.
What are some cost-effective pavement options for a parking lot with moderate traffic?
+
For a parking lot with moderate traffic, asphalt pavement is a cost-effective option. It provides a smooth surface and is relatively easy to maintain. Regular sealing and minor repairs can extend the lifespan of the pavement.
How can I improve the aesthetics of my parking area without compromising functionality?
+
To enhance the aesthetics of your parking area, consider using colored or stamped concrete pavement. These options provide a decorative finish while maintaining the durability and functionality required for parking spaces. Additionally, add landscaping elements and lighting to create a more inviting atmosphere.
What are the benefits of implementing a smart parking system in a commercial parking lot?
+
A smart parking system offers several benefits, including real-time occupancy monitoring, efficient space utilization, and improved customer experience. By providing accurate information on available parking spots, it reduces congestion and enhances the overall efficiency of the parking lot.



