Ultimate Guide: Generate Birmingham Constituency Maps Now
Creating constituency maps for Birmingham can be a complex task, but with the right tools and a systematic approach, it becomes an achievable goal. This guide will take you through the process step by step, ensuring you have all the necessary information to generate accurate and visually appealing maps.
Understanding the Constituency Boundaries
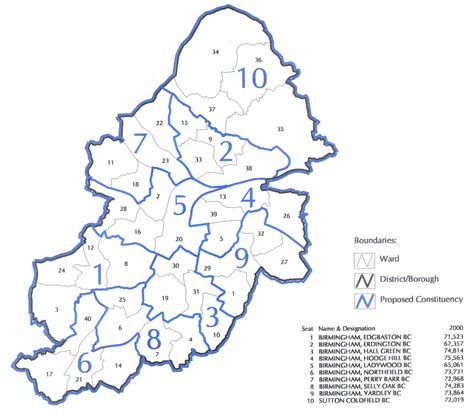
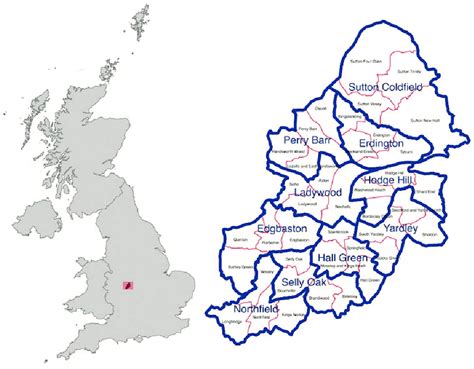
Before diving into the map-making process, it's crucial to grasp the concept of constituency boundaries. In the context of Birmingham, constituencies are geographical areas that are used to elect representatives to the House of Commons in the UK Parliament. These boundaries are periodically reviewed to ensure fair representation and reflect changes in population distribution.
To obtain the latest constituency boundaries for Birmingham, you can refer to the official sources provided by the Boundary Commission for England. They publish detailed maps and data that outline the boundaries of each constituency. It's essential to use the most up-to-date information to ensure accuracy in your maps.
Gathering Data and Resources

To create constituency maps, you'll need a range of data and resources. Here's a checklist to ensure you have everything you need:
- Constituency Boundary Data: As mentioned earlier, this data can be obtained from the Boundary Commission for England. They provide digital boundary files in various formats, including Shapefiles and GeoJSON.
- Geospatial Software: You'll require a software tool that can handle geospatial data and create maps. Popular options include QGIS (an open-source GIS software) and ArcGIS (a commercial GIS platform). Both offer powerful mapping capabilities and are widely used in the industry.
- Base Maps: To provide context and a visual backdrop for your constituency maps, you can utilize base maps. These can be simple road maps, topographic maps, or even satellite imagery. OpenStreetMap and Google Maps are excellent sources for base map data.
- Data Attributes: Depending on the purpose of your maps, you may need additional data attributes. For instance, you might want to include demographic information, election results, or other relevant data. Ensure you have access to these datasets and that they align with your chosen constituency boundaries.
- Design Elements: Consider the visual elements you want to incorporate into your maps. This includes colors, symbols, legends, and labels. Having a clear design plan will make the mapping process more efficient and ensure a consistent look for your final maps.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Constituency Maps
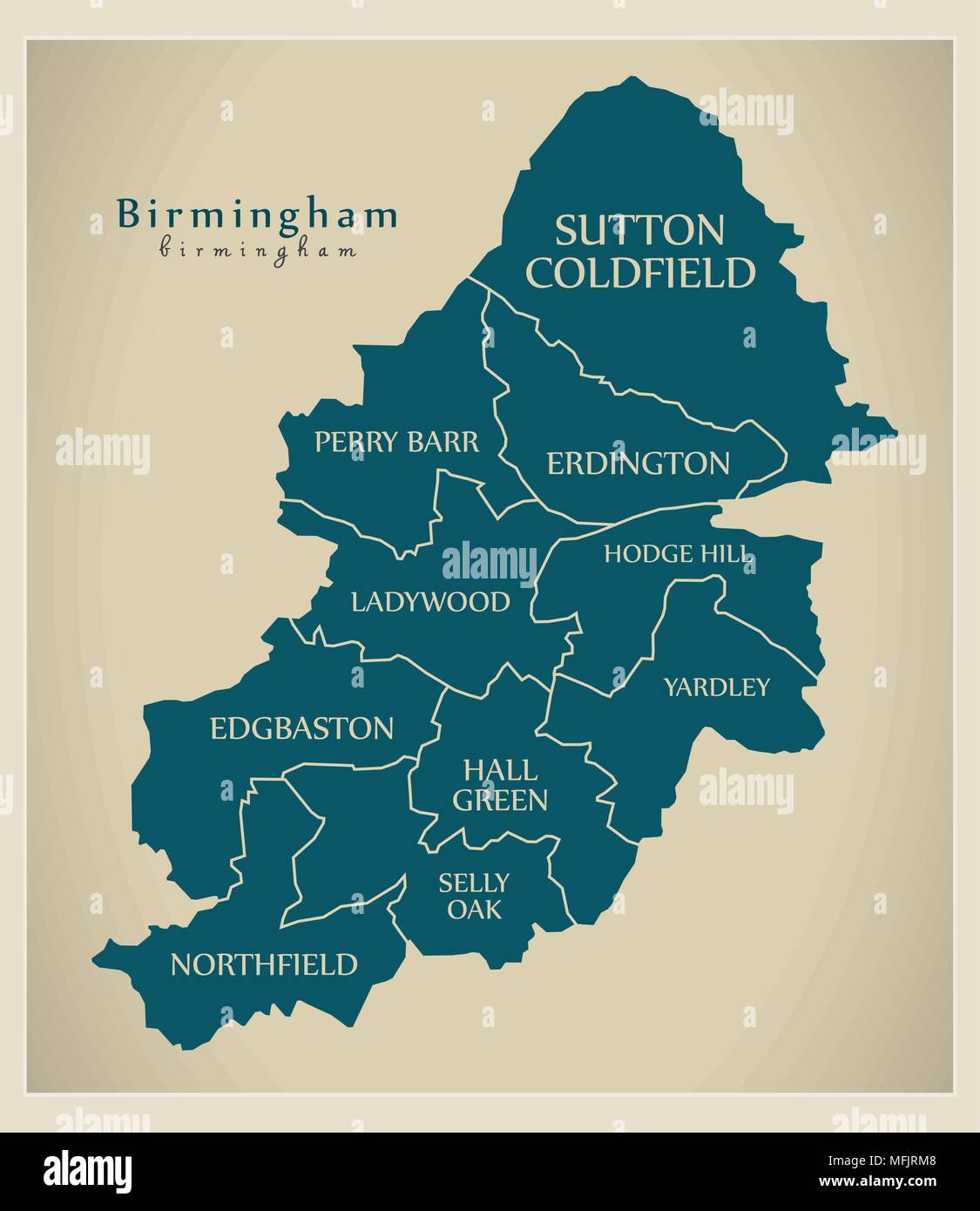
Now, let's dive into the process of generating Birmingham constituency maps using QGIS as an example:
Step 1: Prepare Your Data
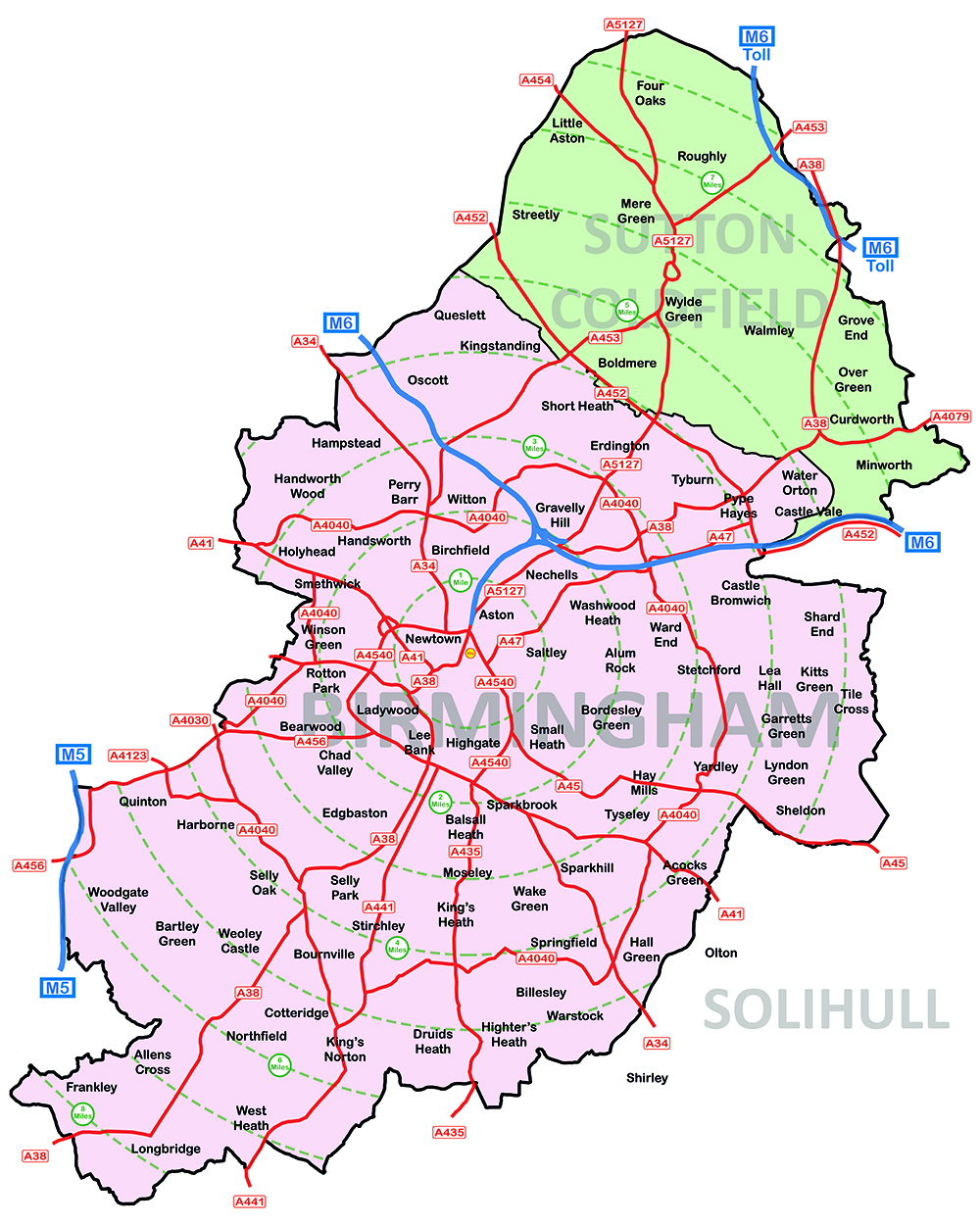
- Download the constituency boundary data from the Boundary Commission for England's website. Ensure you have the latest version.
- Unzip the downloaded files and organize them in a dedicated folder for easy access.
- If your data is in a different format (e.g., CSV or Excel), you may need to convert it into a format compatible with QGIS, such as Shapefile or GeoJSON.
Step 2: Install and Set Up QGIS

- Download and install QGIS from the official website. Choose the version suitable for your operating system.
- Once installed, launch QGIS and familiarize yourself with the interface. Take note of the various toolbars and panels.
- Set up your project by creating a new project or opening an existing one. You can customize the project settings according to your preferences.
Step 3: Add Boundary Data to QGIS

- In the QGIS interface, navigate to the Layer menu and select Add Vector Layer.
- Locate and select the constituency boundary Shapefile or GeoJSON file you downloaded earlier.
- The boundary data will be added to your project, and you should see it in the Layers panel on the left side of the QGIS window.
Step 4: Style Your Map
- Right-click on the constituency boundary layer in the Layers panel and select Properties.
- In the Properties dialog box, navigate to the Style tab.
- Choose an appropriate rendering method (e.g., Simple Fill, Graduated, or Rule-based) based on your data and design preferences.
- Set the fill and outline colors, as well as any other visual attributes, to make your constituencies stand out on the map.
- If you have additional data attributes, you can symbolize them using color gradients, patterns, or labels.
Step 5: Add Base Maps
- Go to the Web menu in QGIS and select Add WMS/WMTS Layer.
- In the Add WMS/WMTS Layer dialog box, enter the URL of the base map service you want to use. You can find these URLs on websites like OpenStreetMap or Google Maps.
- Select the desired base map layer and click Add. The base map will be added to your project, providing a visual context for your constituencies.
Step 6: Customize and Finalize Your Map
- Adjust the transparency of the base map layer to ensure your constituencies remain visible and clear.
- Add labels, legends, and any other design elements to enhance the readability and aesthetics of your map.
- Review your map and make any necessary adjustments to colors, labels, or data attributes.
- Once satisfied with your map, you can export it as an image or PDF file by going to the Project menu and selecting Save as Image or Save as PDF.
Advanced Tips and Tricks
Here are some additional tips to take your constituency maps to the next level:
- Symbolize Data: Experiment with different visualization techniques to represent data attributes. This could include using choropleth maps, proportional symbols, or graduated symbols.
- Layer Transparency: Adjust the transparency of layers to create a balanced and visually appealing map. This is especially useful when dealing with multiple layers or complex data.
- Map Projections: Consider the map projection you use. Different projections can impact the visual representation of your constituencies, so choose one that best suits your purpose.
- Legend and Labels: Create a clear and concise legend to explain the symbols and colors used on your map. Ensure labels are easy to read and provide necessary information without overcrowding the map.
- Map Scale: Determine the appropriate map scale for your constituencies. A larger scale may provide more detail, while a smaller scale offers a broader overview.
Conclusion
Generating Birmingham constituency maps is an exciting and rewarding endeavor. By following this comprehensive guide, you now have the knowledge and tools to create accurate and visually appealing maps. Remember to stay up-to-date with the latest constituency boundaries and explore the vast possibilities offered by geospatial software like QGIS. With a bit of practice and creativity, you can produce maps that effectively communicate the political landscape of Birmingham.
How often are constituency boundaries reviewed and updated?

+
Constituency boundaries are typically reviewed every 5 to 8 years by the Boundary Commission for England. These reviews ensure fair representation and address changes in population distribution.
Can I use other GIS software besides QGIS and ArcGIS?
+
Yes, there are several other GIS software options available, such as MapInfo and GRASS GIS. The steps and processes may vary, but the core principles of map creation remain similar.
Are there any online tools for creating constituency maps?

+
While there are online mapping platforms, they may have limitations compared to dedicated GIS software. However, tools like Mapbox and Carto offer user-friendly interfaces for creating basic maps.
How can I add demographic data to my constituency maps?
+
To include demographic data, you’ll need to obtain relevant datasets from reliable sources. Once you have the data, you can join it with your constituency boundary data and symbolize it on your maps.
What are some best practices for map design?
+Keep your maps simple and focused. Use a limited color palette and avoid clutter. Ensure labels and legends are clear and easy to understand. Consider the purpose of your map and design it accordingly.



