20+ Parliamentary Seats: The Ultimate Guide To Understanding Uk Politics

The Complex World of UK Politics: An In-Depth Exploration

The United Kingdom’s political landscape is intricate and multifaceted, with a unique parliamentary system that shapes its governance. Understanding the dynamics of UK politics is essential for anyone interested in current affairs, as it influences not only domestic policies but also the country’s global standing. This guide aims to demystify the key aspects of UK politics, from its historical roots to the contemporary challenges it faces.
The Foundation: A Historical Perspective

To grasp the complexities of modern UK politics, it’s crucial to delve into its historical context. The British political system has evolved over centuries, shaped by a rich tapestry of events and influences. Here’s a brief overview:
Monarchical Rule: The UK’s political history can be traced back to the medieval period, where power was primarily held by monarchs. The monarchy played a central role in governance, with kings and queens often exerting absolute authority.
The Magna Carta: One of the most significant milestones in UK political history is the Magna Carta, signed in 1215. This document, forced upon King John by a group of barons, established the principle of the rule of law and limited the power of the monarchy. It laid the foundation for constitutional monarchy and the protection of individual rights.
Parliament’s Rise: Over time, the power of the monarchy waned, and the role of Parliament grew. The English Civil War (1642-1651) and the Glorious Revolution (1688) further solidified Parliament’s position as the primary legislative body. These events led to the establishment of a constitutional monarchy, where the monarch’s powers were significantly reduced.
The Act of Union: In 1707, the Act of Union brought together the Kingdoms of England and Scotland, creating the Kingdom of Great Britain. This union had a profound impact on the political landscape, leading to the formation of a unified Parliament and the emergence of a new political class.
The Industrial Revolution: The 18th and 19th centuries saw the UK undergo significant social and economic changes with the Industrial Revolution. This period witnessed the rise of new political ideologies, such as liberalism and socialism, and the expansion of voting rights, leading to a more inclusive democracy.
The UK’s Parliamentary System: A Unique Structure

The UK’s parliamentary system is a cornerstone of its political landscape. It is a form of representative democracy, where elected officials, known as Members of Parliament (MPs), make decisions on behalf of the people. Here’s a breakdown of its key features:
The Houses of Parliament: The UK’s Parliament consists of two chambers: the House of Commons and the House of Lords. The House of Commons is the lower house, comprising elected MPs, while the House of Lords is the upper house, made up of appointed or hereditary peers.
General Elections: General elections are held to elect MPs to the House of Commons. These elections occur at least every five years, and the party that wins a majority of seats forms the government. If no party gains a majority, a coalition government may be formed.
First-Past-the-Post (FPTP) System: The UK uses the FPTP electoral system, where the candidate with the most votes in a constituency wins. This system has been criticized for not always reflecting the popular vote accurately, as it can lead to “safe seats” and the “wasted vote” phenomenon.
The Prime Minister: The leader of the majority party in the House of Commons becomes the Prime Minister, the head of the government. The Prime Minister appoints a cabinet of ministers, who are responsible for different government departments.
The Monarch’s Role: While the monarch’s political powers are limited, they still play a ceremonial and symbolic role. The monarch formally appoints the Prime Minister and grants Royal Assent to legislation, but they act on the advice of the Prime Minister and ministers.
Understanding Political Parties
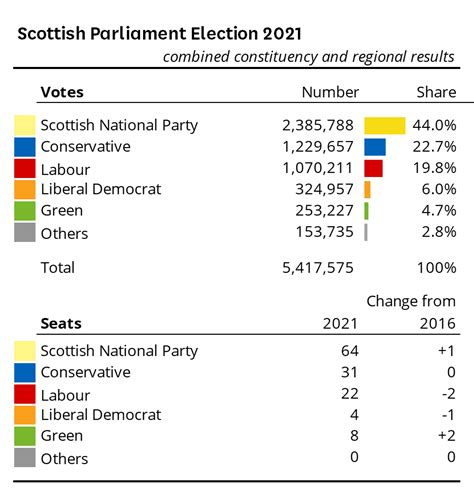
UK politics is dominated by a two-party system, with the Conservative Party and the Labour Party being the two major political forces. However, there are also several smaller parties that play a significant role, especially in specific regions:
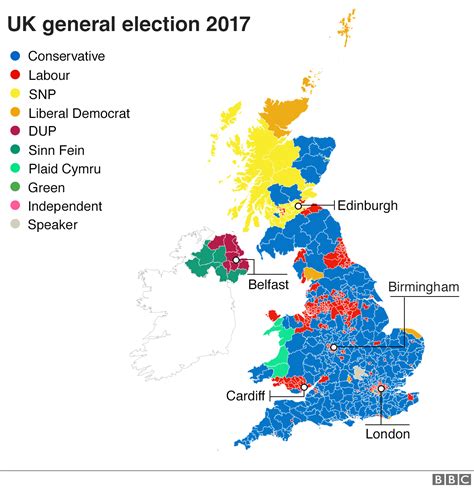
Conservative Party: Often referred to as the Tories, the Conservative Party is a centre-right political party. It has a long history, dating back to the 1830s, and has held power for much of the UK’s modern history. The Conservatives generally advocate for free-market economics, small government, and traditional values.
Labour Party: The Labour Party is a centre-left political party, founded in the late 19th century to represent the interests of the working class. It has traditionally focused on social justice, workers’ rights, and state intervention in the economy. The Labour Party has held power at various times, notably under Prime Ministers Clement Attlee and Tony Blair.
Liberal Democrats: The Liberal Democrats, or Lib Dems, are a centrist political party formed from the merger of the Liberal Party and the Social Democratic Party. They advocate for civil liberties, proportional representation, and a mixed economy. The Lib Dems have often played a pivotal role in coalition governments.
Scottish National Party (SNP): The SNP is a Scottish nationalist party that campaigns for Scottish independence. It has gained significant support in recent years, winning a majority of Scottish seats in the 2015 and 2017 general elections. The SNP’s rise has had a major impact on UK politics, particularly in the context of Brexit.
Other Parties: There are numerous smaller parties in the UK, including the Green Party, which focuses on environmental issues, and the UK Independence Party (UKIP), which advocates for a hard Brexit and a more restrictive immigration policy. These parties often have regional strongholds and can influence the outcome of elections.
The Impact of Brexit

Brexit, the UK’s decision to leave the European Union (EU), has been one of the most significant political events of recent times. The referendum on Brexit, held in 2016, resulted in a narrow majority voting to leave the EU. Since then, Brexit has dominated UK politics, shaping policy decisions and causing significant divisions.
Negotiations and Deadlines: The process of negotiating the terms of Brexit has been complex and fraught with challenges. The UK and the EU have had to navigate issues such as trade agreements, the Irish border, and the rights of EU citizens in the UK. Multiple deadlines for Brexit have been set and extended, with the final withdrawal date being January 31, 2020.
Political Instability: Brexit has caused considerable political instability, with several Prime Ministers resigning or being ousted due to their handling of the issue. The Conservative Party, in particular, has faced internal divisions, leading to leadership challenges and a shift in party policies.
Impact on UK Politics: Brexit has had a profound impact on UK politics, reshaping the political landscape. It has led to a rise in populist and nationalist sentiments, with issues like immigration and sovereignty taking center stage. The Brexit debate has also highlighted the divide between urban and rural areas, as well as between younger and older voters.
Contemporary Challenges and Issues
UK politics is currently grappling with a range of complex challenges and issues, many of which have been exacerbated by Brexit:
Economic Uncertainty: The UK’s decision to leave the EU has created economic uncertainty, with potential impacts on trade, investment, and financial markets. The government is working to negotiate new trade deals and mitigate the economic consequences of Brexit.
Social Inequality: Social inequality remains a significant issue in the UK, with disparities in income, wealth, and opportunities. The government has pledged to address these inequalities through policies aimed at improving social mobility and reducing poverty.
Climate Change: The UK has set ambitious targets to reduce carbon emissions and transition to a low-carbon economy. The government is implementing policies to promote renewable energy, improve energy efficiency, and encourage sustainable practices.
Healthcare and Social Care: The National Health Service (NHS) is a cornerstone of UK society, but it faces significant challenges, including funding shortages and an aging population. The government is investing in healthcare infrastructure and exploring ways to improve access to quality healthcare.
Education Reform: The UK’s education system is undergoing reforms to address issues such as teacher shortages, curriculum updates, and improving outcomes for disadvantaged students. The government is focusing on raising standards and providing equal opportunities for all.
The Future of UK Politics
As the UK navigates the post-Brexit era, its political landscape is likely to undergo further transformations. Here are some key trends and predictions:
Political Polarization: Brexit has contributed to a more polarized political environment, with deep divisions between those who support leaving the EU and those who wish to remain. This polarization is likely to continue, shaping future political debates and elections.
Regional Devolution: The rise of regional parties, particularly the SNP, has led to calls for greater devolution of powers to Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. The UK government is likely to face increasing pressure to accommodate these demands, potentially leading to a more decentralized political system.
Electoral Reform: The FPTP electoral system has come under scrutiny, with critics arguing that it does not accurately represent the will of the people. There are growing calls for electoral reform, with some advocating for a move to a proportional representation system.
Green Agenda: Climate change and environmental issues are likely to remain at the forefront of UK politics. The government is expected to continue its efforts to transition to a greener economy, with a focus on renewable energy and sustainable practices.
Social Justice and Equality: The UK’s commitment to social justice and equality is likely to be tested in the coming years. The government will need to address issues such as racial inequality, gender equality, and LGBTQ+ rights, especially in the context of post-Brexit Britain.
Notes:

📢 Note: This guide provides a comprehensive overview of UK politics, but it is a vast and ever-evolving topic. Stay informed by following reputable news sources and engaging in political discussions to deepen your understanding.
Conclusion

Understanding UK politics is a complex yet rewarding endeavor. From its rich historical foundations to the contemporary challenges it faces, the UK’s political landscape is a dynamic and fascinating subject. By exploring the key aspects outlined in this guide, readers can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of UK governance and its impact on both domestic and global affairs. As the UK navigates its post-Brexit future, staying informed and engaged is more important than ever.
FAQ

What is the role of the House of Lords in the UK’s parliamentary system?
+
The House of Lords is the upper chamber of the UK Parliament. It consists of appointed or hereditary peers who scrutinize legislation and can propose amendments. While the House of Lords has less power than the House of Commons, it plays a crucial role in the legislative process, providing a check on the government’s power.
How often are general elections held in the UK?

+
General elections in the UK are held at least every five years, but the Prime Minister can call an election earlier if they believe it is in the best interest of the country. The election date is set by the Prime Minister, and the campaign period typically lasts around six weeks.
What is the impact of Brexit on the UK’s relationship with the European Union (EU)?
+
Brexit has significantly impacted the UK’s relationship with the EU. The UK is no longer a member of the EU, which means it is no longer bound by EU laws and regulations. The UK and the EU are now negotiating new trade agreements and establishing a new framework for their relationship, which includes issues such as trade, immigration, and security.
How does the UK’s political system compare to other democracies around the world?

+
The UK’s parliamentary system is unique compared to other democracies. While many countries have a two-chamber parliament, the UK’s system is characterized by its first-past-the-post electoral system and the role of the monarch. The UK’s system is often compared to the US’s presidential system, but there are key differences, such as the absence of a written constitution in the UK.
What are some of the key challenges facing the UK’s political system in the future?
+The UK’s political system faces several challenges in the future, including political polarization, the rise of regional parties, and the need for electoral reform. Additionally, the UK will need to navigate its post-Brexit relationship with the EU and address issues such as economic uncertainty, social inequality, and climate change.



